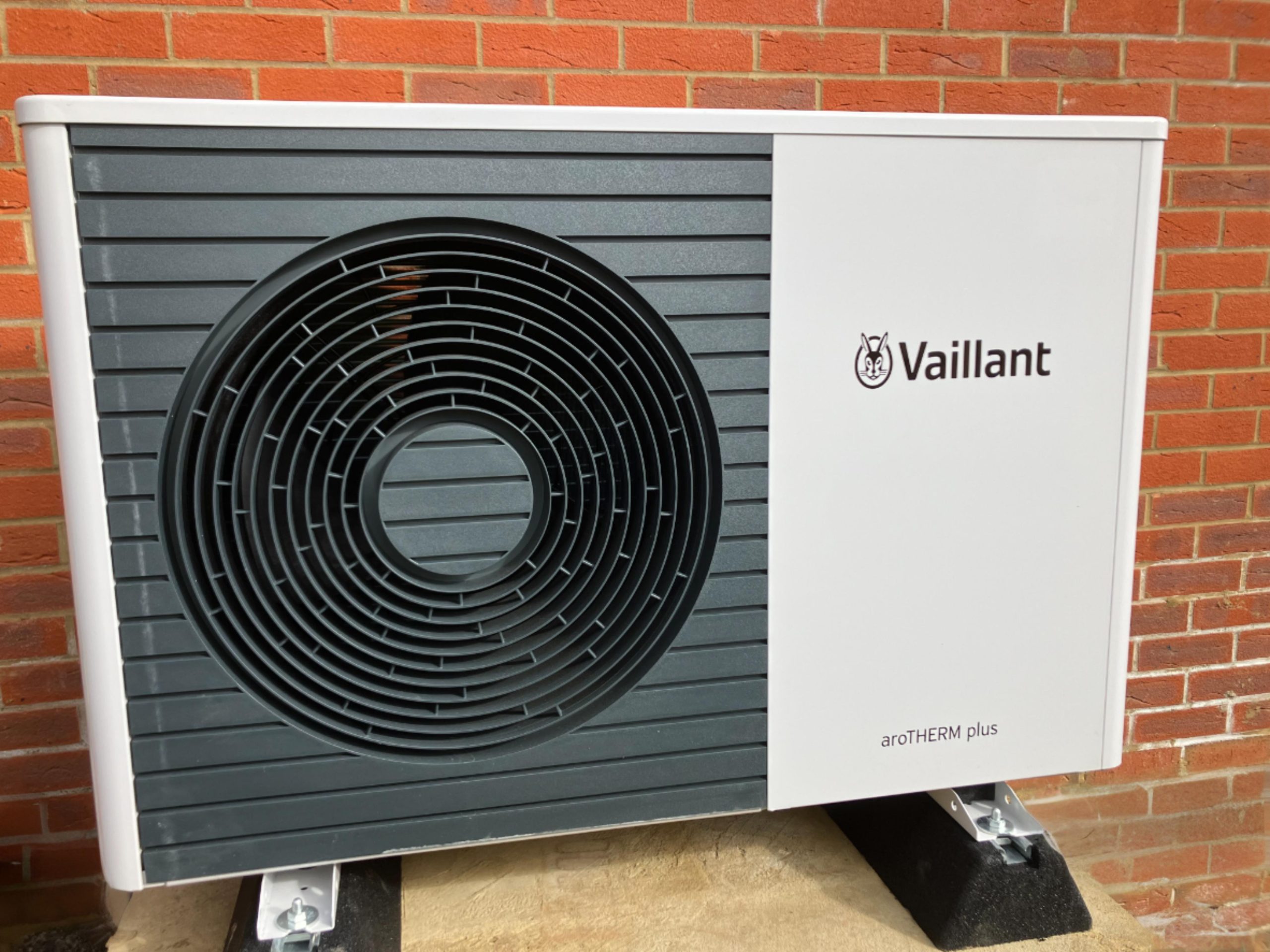
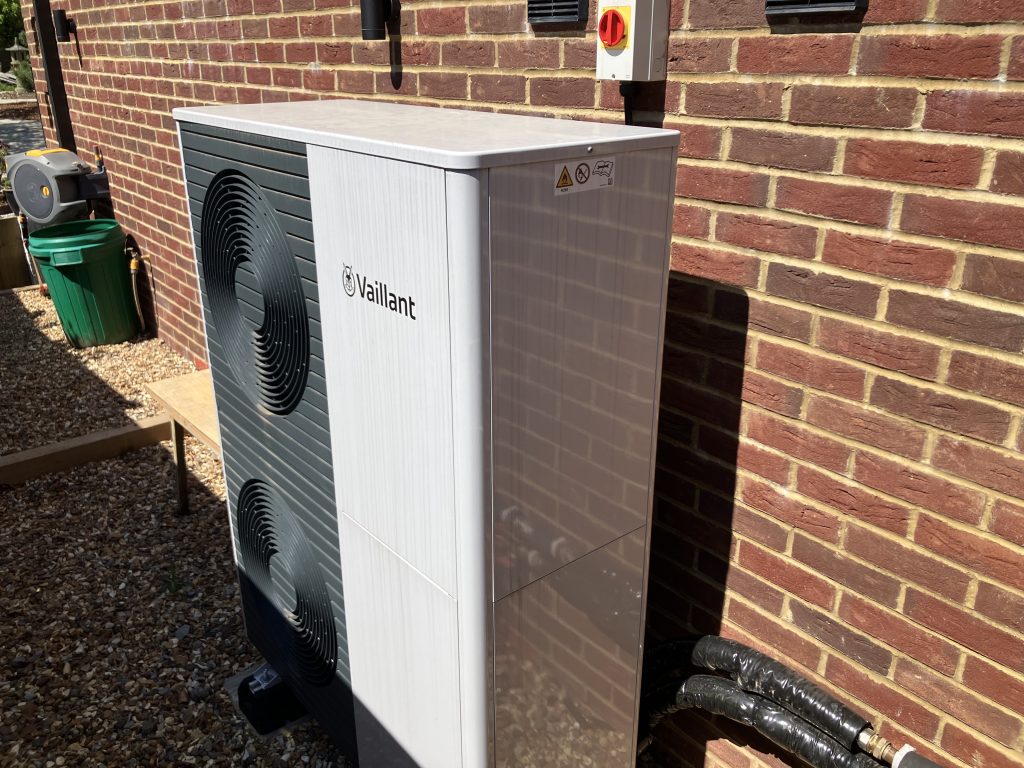
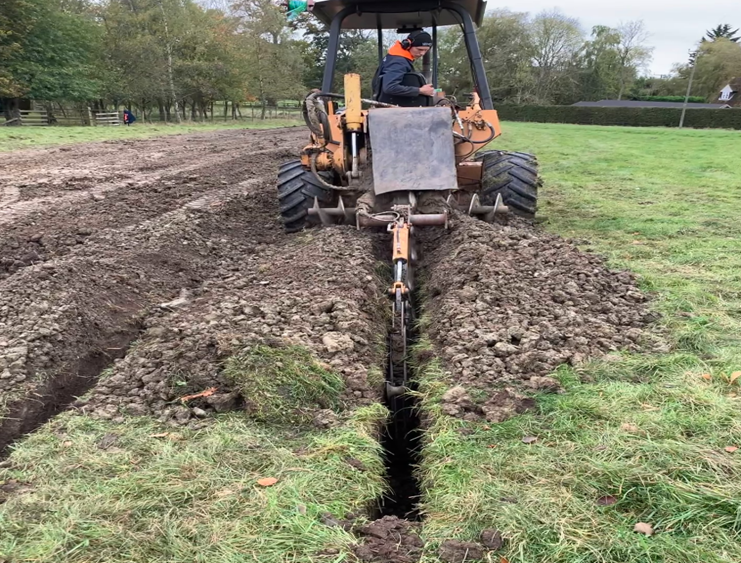
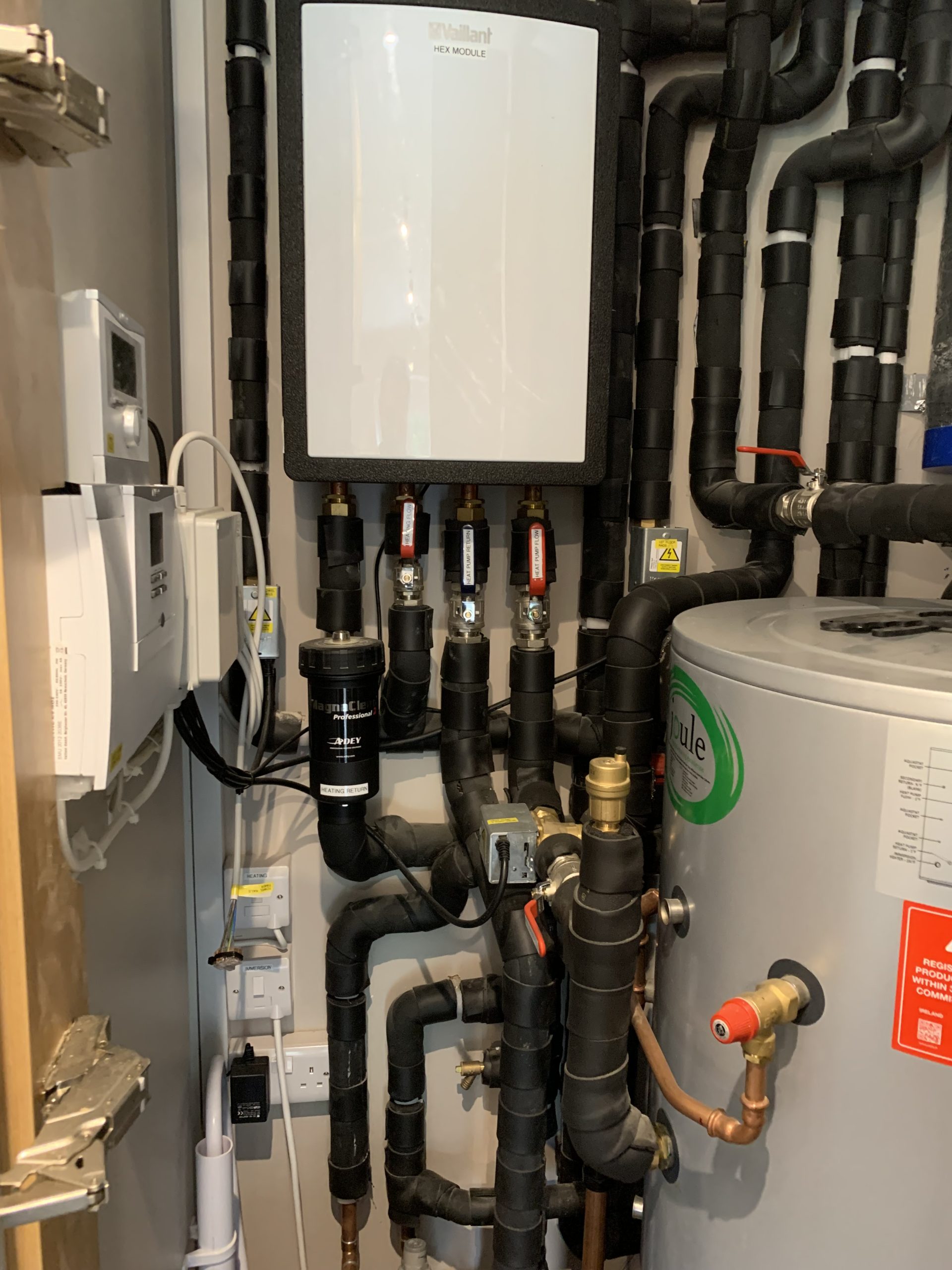
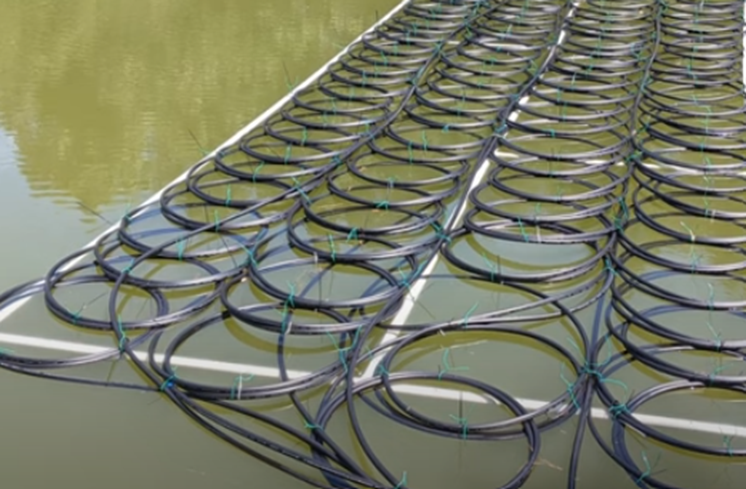
Heat pumps are versatile devices that can both heat and cool your home by transferring heat energy between indoor and outdoor environments. Using a refrigeration cycle, they extract heat from the air, ground, or water and transfer it to where it’s needed. There are several types of heat pumps, including air-source, ground-source, and water-source models, each with unique features and applications suited to different climates and building types.
The efficiency of heat pumps is typically measured by their Coefficient of Performance (COP) for heating. A higher COP indicates better performance, meaning the system uses less electricity to provide the desired heating or cooling output, improving sustainability. Heat pumps are an environmentally friendly option, as they significantly reduce carbon emissions compared to traditional fossil fuel-based systems and help combat climate change. They can also integrate with renewable energy sources like solar panels to further enhance sustainability and improve energy efficiency. Additionally, heat pumps offer long-term savings by lowering energy bills, reducing reliance on fossil fuels, and providing consistent indoor comfort throughout the year in all seasons.